Table of Contents
Section 2.1. Using JWTs as Authorization Grants of RFC 7523 JSON Web Token (JWT) Profile for OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication and Authorization Grants defines another flow for access token issuance which is different from OAuth 2.0 standard flows defined in RFC 6749. We call it JWT Authorization Grant flow.
In the flow, a JWT (RFC 7519) is used as an authorization grant, which indicates that its holder has been authorized to get an access token. The JWT as an authorization grant is the same concept as an authorization code in the authorization code flow (RFC 6749 Section 4.1).
To obtain an access token, the requester presents a JWT at the token endpoint (RFC 6749 Section 3.2). The following diagram illustrates this flow:
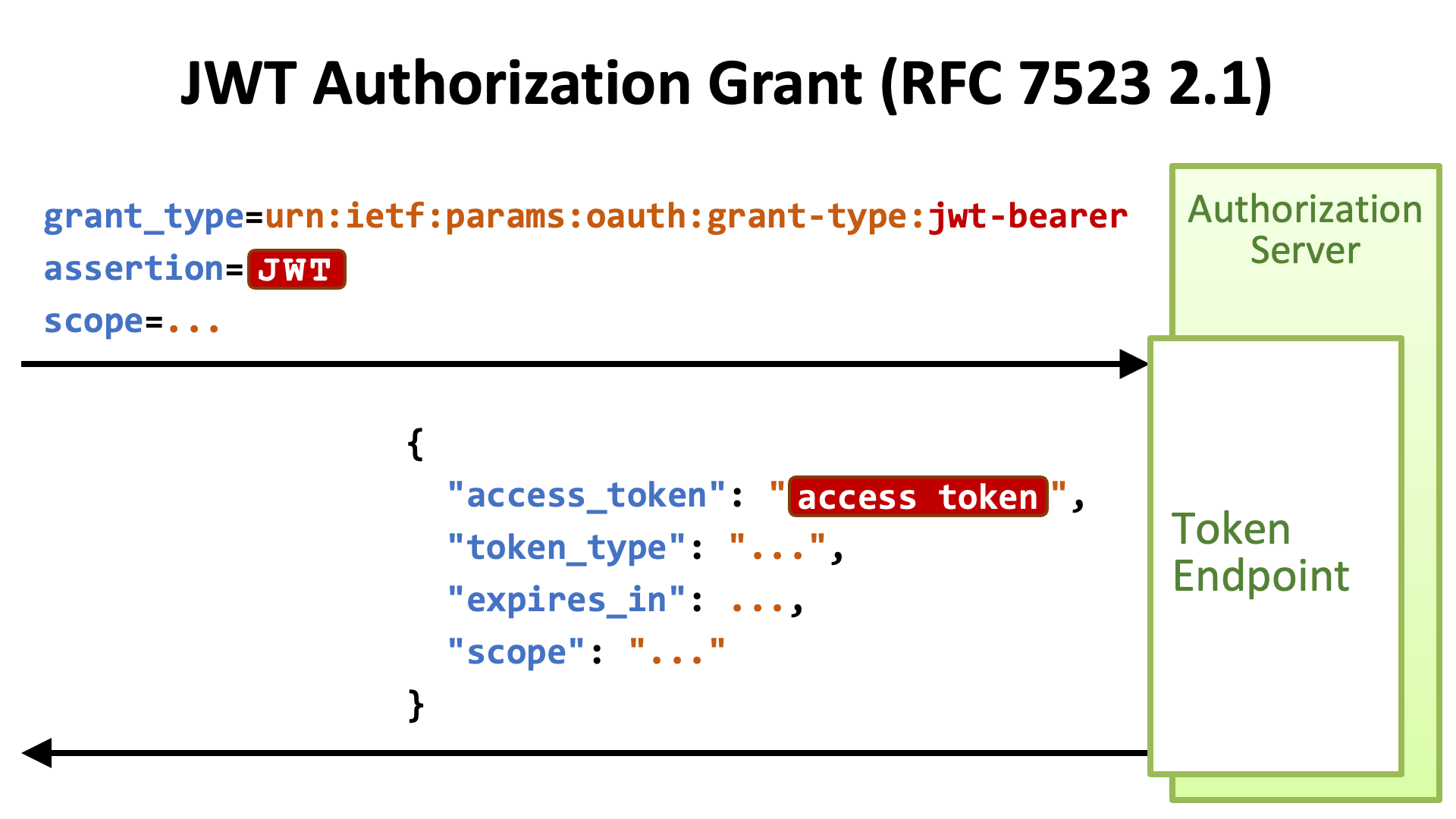
RFC 7523 does not define details about how the JWT as an authorization grant is generated by whom. Consequently, it is not defined in the specification how to obtain the key whereby to verify the signature of the JWT. Therefore, each deployment has to define their own rules which are necessary to identify the key for signature verification.
For example, some systems may define a rule like “The JWT must be an ID Token issued by https://example.com”. If a JWT is an ID Token, authorization server implementations can find the key for signature verification by using the standard mechanism (i.e. the discovery endpoint and the jwks_uri server metadata). Other systems may choose to embed the key for signature verification in the JWT itself as entity statements of OpenID Connect Federation 1.0 do.
In any case, systems must define additional rules to complement RFC 7523 when they employ the specification.
To distinguish the JWT authorization grant flow from others, the specification has defined a new grant type urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. The value is used as the value of the grant_type request parameter of a token request.
The specification does not require client authentication and even client identification at the token endpoint. The specification states it as follows.
JWT authorization grants may be used with or without client authentication or identification.
Technically speaking, “with or without client authentication” means that the specification does not care about whether the client type (RFC 6749 Section 2.1) of the client application is public or confidential, and “without client identification” means that a token request does not contain information whereby to identify the client application making the request (e.g. lack of the client_id request parameter).
A token request of the JWT authorization grant flow may have the scope request parameter to specify scopes to request as the standard OAuth 2.0 flows may do.
A JWT used as an authorization grant is specified by the assertion request parameter, which is defined in Section 4.1. Using Assertions as Authorization Grants of RFC 7521 Assertion Framework for OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication and Authorization Grants.
The table below is a summary about necessity of JWT claims. Detailed requirements on the claims are described in Section 3 of RFC 7523.
| Claim | Necessity |
|---|---|
iss |
REQUIRED |
sub |
REQUIRED |
aud |
REQUIRED |
exp |
REQUIRED |
nbf |
OPTIONAL |
iat |
OPTIONAL |
jti |
OPTIONAL |
The following is an example listed in Section 2.1 of RFC 7523.
POST /token.oauth2 HTTP/1.1
Host: as.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Ajwt-bearer
&assertion=eyJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjE2In0.
eyJpc3Mi[...omitted for brevity...].
J9l-ZhwP[...omitted for brevity...]
Token responses in the JWT authorization grant flow conform to RFC 6749. No additional response parameters are defined by RFC 7523.
Only point to note is that invalid_grant must be used as the value of the error response parameter when the given JWT is invalid.
JWT authorization grant flow is supported by Authlete 2.3 onwards.
/auth/token APITo support JWT authorization grant flow, a new action value JWT_BEARER was added. When the value of the grant_type request parameter of a token request is urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer and the request passes basic validation steps which are performed on Authlete server side, the value of the action response parameter in the response from Authlete’s /auth/token API holds JWT_BEARER.
Authorization server implementations have to process the JWT_BEARER action to support JWT authorization grant flow. The switch statement below excerpted from TokenRequestHandler.java in the authlete-java-jaxrs library is an example of processing the JWT_BEARER action. The switch statement has a case entry for JWT_BEARER.
// Dispatch according to the action.
switch (action)
{
case INVALID_CLIENT:
// 401 Unauthorized
return ResponseUtil.unauthorized(content, CHALLENGE);
case INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR:
// 500 Internal Server Error
return ResponseUtil.internalServerError(content);
case BAD_REQUEST:
// 400 Bad Request
return ResponseUtil.badRequest(content);
case PASSWORD:
// Process the token request whose flow is "Resource Owner Password Credentials".
return handlePassword(response);
case OK:
// 200 OK
return ResponseUtil.ok(content);
case TOKEN_EXCHANGE:
// Process the token exchange request (RFC 8693)
return handleTokenExchange(response);
case JWT_BEARER:
// Process the token request which uses the grant type
// urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer (RFC 7523).
return handleJwtBearer(response);
default:
// This never happens.
throw getApiCaller().unknownAction("/api/auth/token", action);
}
The following table lists response parameters related to JWT authorization grant in a response from the /auth/token API.
| Response Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
assertion |
string | The value of the assertion request parameter of the token request. |
scopes |
string array | The value of the scope request parameter of the token request. |
When the grant type of a token request is urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer, Authlete (to be exact, the implementation of Authlete’s /auth/token API) performs validation steps listed below in the order. Therefore, authorization server implementations can omit the same validation steps.
| No. | Validation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm that the assertion request parameter is given and its value is not empty. |
| 2 | Confirm that the format conforms to the JWT specification (RFC 7519 JSON Web Token (JWT)). |
| 3 | Check if the JWT is encrypted and if it is encrypted, then (a) reject the token request when the jwtGrantEncryptedJwtRejected flag of the service is true or (b) skip remaining validation steps when the flag is false. |
| 4 | Confirm that the JWT contains the iss claim and its value is a JSON string. |
| 5 | Confirm that the JWT contains the sub claim and its value is a JSON string. |
| 6 | Confirm that the JWT contains the aud claim and its value is either a JSON string or an array of JSON strings. |
| 7 | Confirm that the issuer identifier of the service (the issuer server metadata) or the URL of the token endpoint (the token_endpoint server metadata) is listed as audience in the aud claim. |
| 8 | Confirm that the JWT contains the exp claim and the current time has not reached the time indicated by the claim. |
| 9 | Confirm that the current time is equal to or after the time indicated by the iat claim if the JWT contains the claim. |
| 10 | Confirm that the current time is equal to or after the time indicated by the nbf claim if the JWT contains the claim. |
| 11 | Check if the JWT is signed and if it is not signed, then (a) reject the token request when the jwtGrantUnsignedJwtRejected flag of the service is true or (b) finish validation on the JWT. |
To configure options related to the JWT Authorization Grant, follow these steps:
Log in to the Authlete Management Console.
Navigate to Service Settings > Endpoints > Token > JWT Authz Grant.
The following options are available for configuration:
| Configuration Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Client ID | Toggle this option to reject token requests that do not include a client identifier. |
| Encrypted JWT | Toggle this option to allow or reject token requests using encrypted JWTs as authorization grants. |
| Unsigned JWT | Toggle this option to allow or reject token requests using unsigned JWTs as authorization grants. |

JwtAuthzGrantProcessor.java in java-oauth-server, an open-source sample implementation of authorization server written in Java, is a sample implementation of processing a token request of the JWT authorization grant flow.
Note that the implementation is just an example and does not intend to be perfect for commercial use.
1. Prepare a JWT in some way or other.
$ JWT=eyJraWQiOiJhdXRobGV0ZS1mYXBpZGV2LWFwaS0yMDE4MDUyNCIsImFsZyI6IlJTMjU2In0.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2ZhcGlkZXYtYXMuYXV0aGxldGUubmV0LyIsInN1YiI6IjEwMDQiLCJhdWQiOlsiNTg5OTQ2MzYxNDQ0ODA2MyJdLCJleHAiOjE2NTg2NzExMzAsImlhdCI6MTY1ODY3MDgzMCwiYXV0aF90aW1lIjoxNjU4NjcwODMwLCJub25jZSI6IjEyMzQ1Njc4OSIsInZlcmlmaWVkX2NsYWltcyI6eyJ2ZXJpZmljYXRpb24iOnsidHJ1c3RfZnJhbWV3b3JrIjoibmlzdF84MDBfNjNBIn0sImNsYWltcyI6eyJnaXZlbl9uYW1lIjoiSW5nYSIsImZhbWlseV9uYW1lIjoiU2lsdmVyc3RvbmUiLCJiaXJ0aGRhdGUiOiIxOTkxLTExLTA2IiwiOmFnZV8xOF9vcl9vdmVyIjpudWxsfX19.mxE8FQaDb0edY_rWasSQ7pEMXbFon7oWr-Ccv1dB15q8eh2MaKRGrgvwPw_XjAdXlMNzkcV6iEUjRUvLGTvzm7_45cdoOxRX1xWzQw-vwvRbM46xd3Yht3EVjyRUUBJ_92J1yBmu7Nn93rygcnCE-fC_bSTSIJWgEnoC7dpxHYnoJ2QHrIOYFMBAA_3ZYCLGpgiWbIZnB2D1ib2eqwJ9zoJqeFNEBhXo9ThYkASHYaG-ZWofy7364lgeV4Rqy1r4XqzchFRW4yzWs_IM72bTtXTUkstlNOxZU12KEz50uVhtcOXv06iI71I9vceRP-ZVICpq7Knt0vEKWTM41E3ziw
2. Make a token request.
$ curl http://localhost:8080/api/token -d grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer -d assertion=$JWT -d client_id=5908895171 -d scope=email
3. Receive a token response.
{
"access_token":"NEdL-q9EfOI4S5XzaMeimXAXVqS139Jm9DTYeLUAd5o",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":86400,
"scope":"email"
}