Table of Contents
OpenID Connect Native SSO for Mobile Apps 1.0 (hereafter referred to as “Native SSO”) is a standard specification that defines a mechanism for achieving single sign-on (SSO) across multiple mobile applications under the control of the same vendor. If this specification is implemented, users are not required to authenticate individually for each mobile application; instead, a single authentication suffices for all applications integrated via Native SSO.
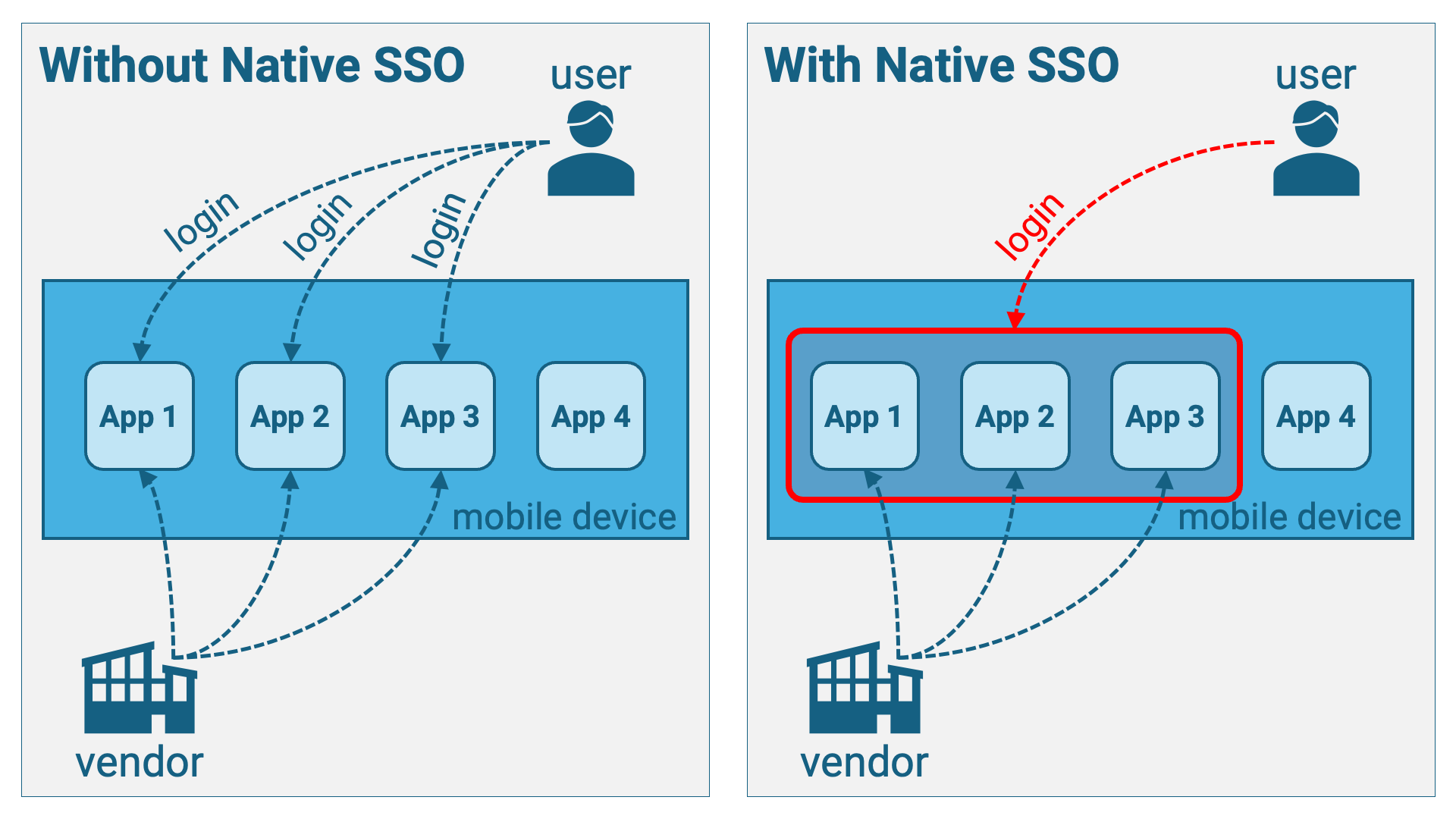
Before diving into the details, let’s start with an overview of the specification.
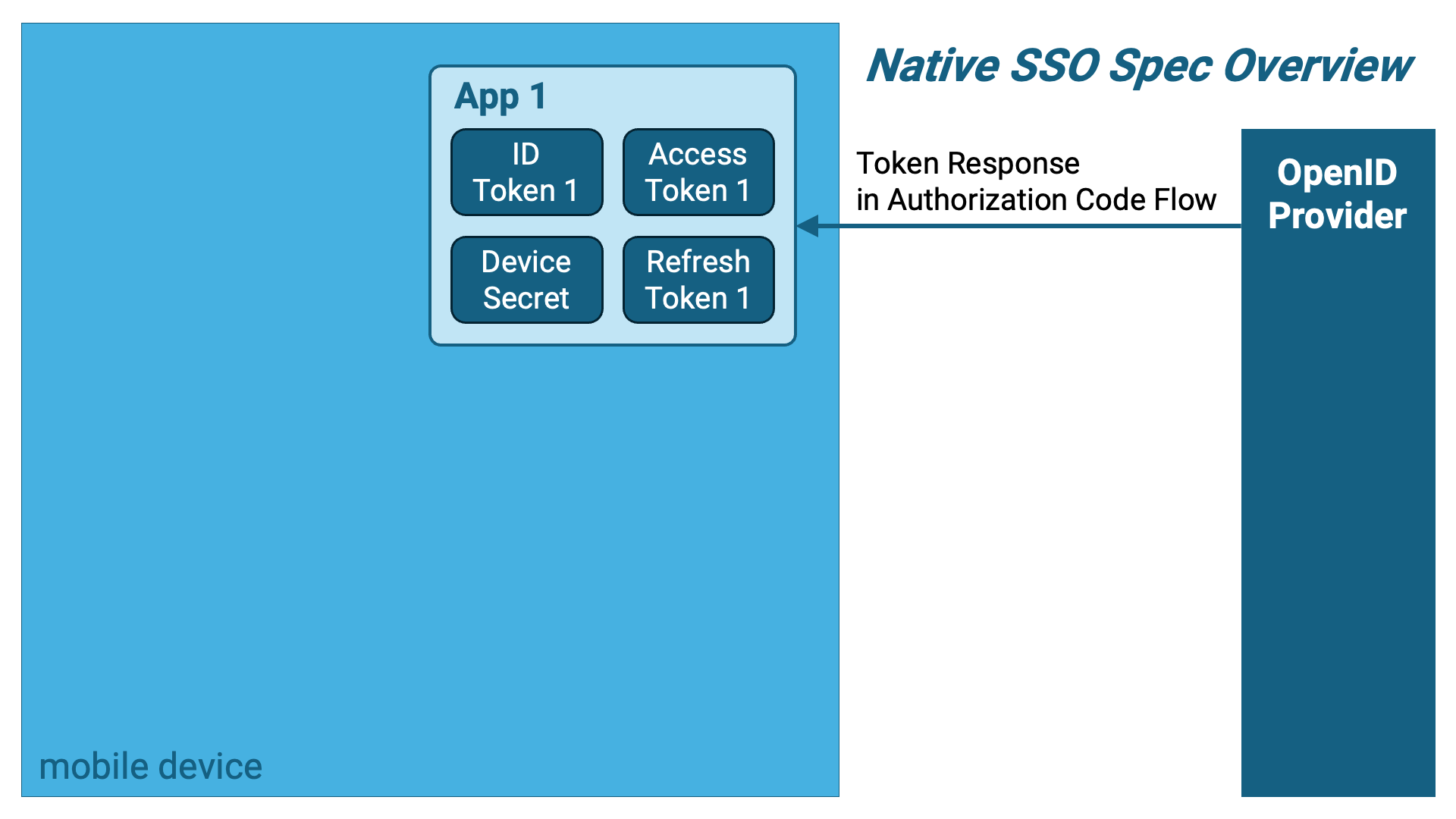
The first application (hereafter referred to as “App 1”) obtains the following set of tokens using the authorization code flow. Notably, the ID token conforms to the Native SSO specification, and a new type of token called a device secret is included.
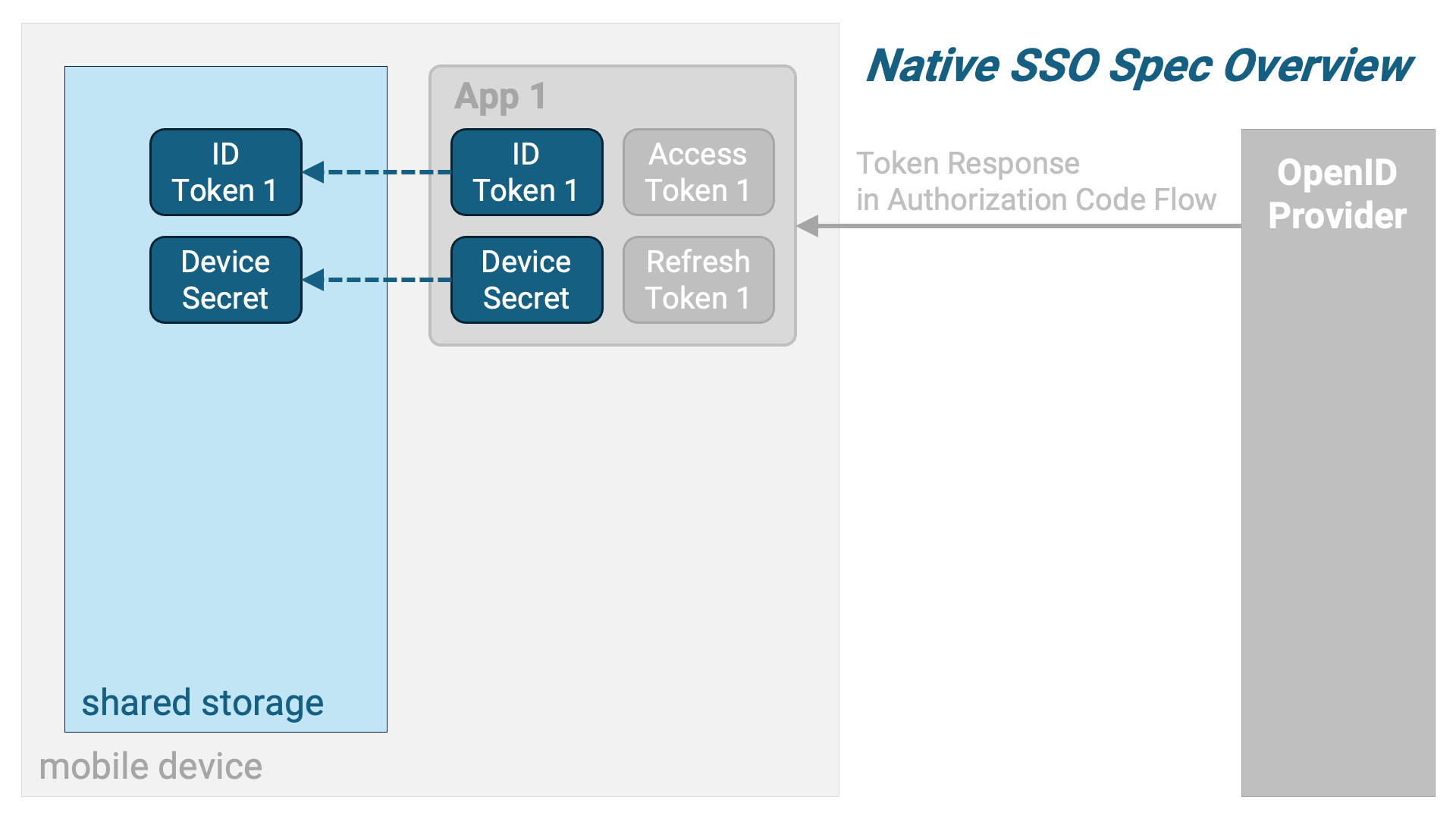
App 1 stores the ID token and the device secret in shared storage that the second application (hereafter referred to as “App 2”) can access.
Next, App 2 retrieves the ID token and device secret from the shared storage and sends a token exchange request using them as parameters.
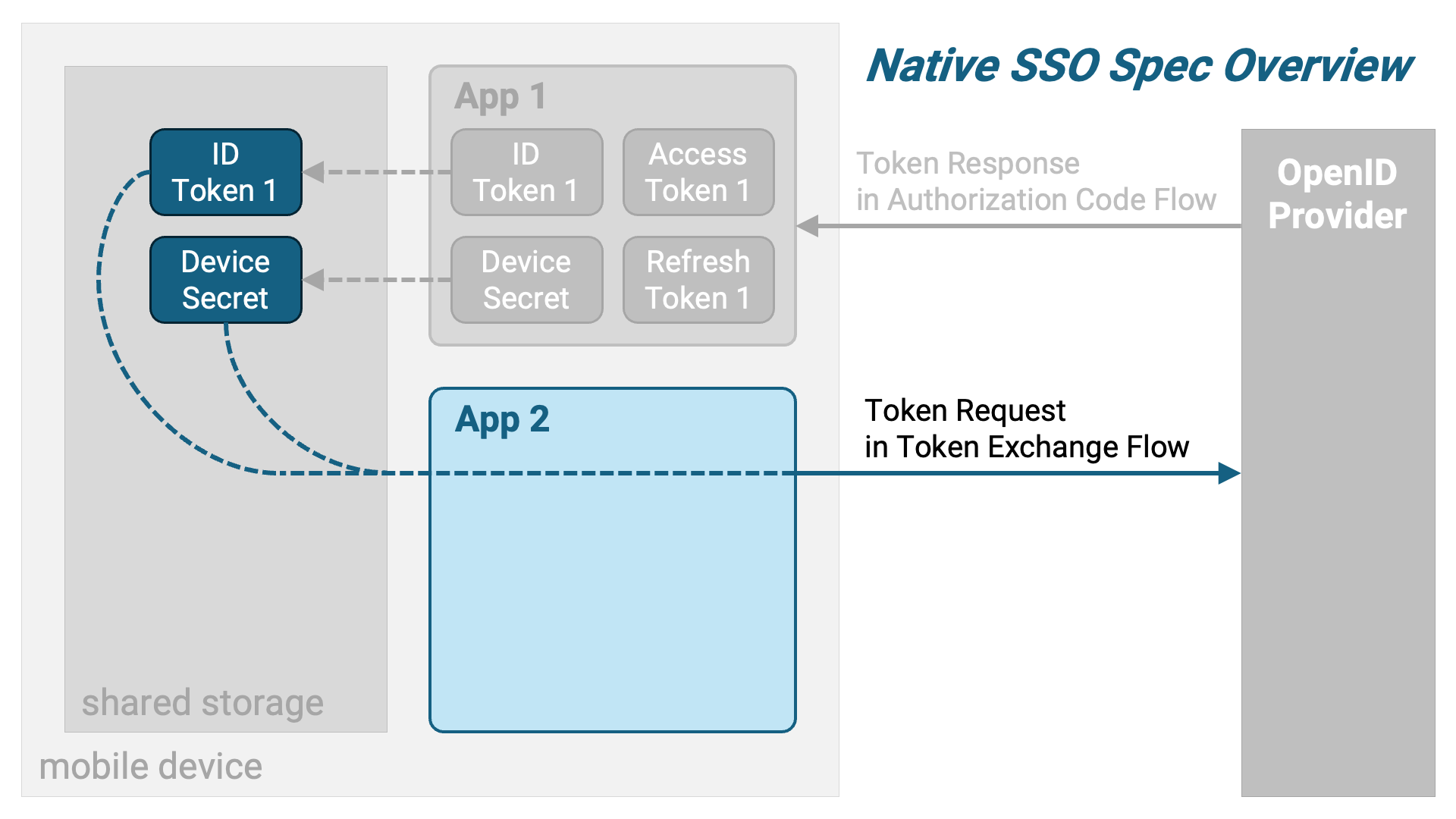
In response, a token exchange response containing a new set of tokens for App 2 is returned.
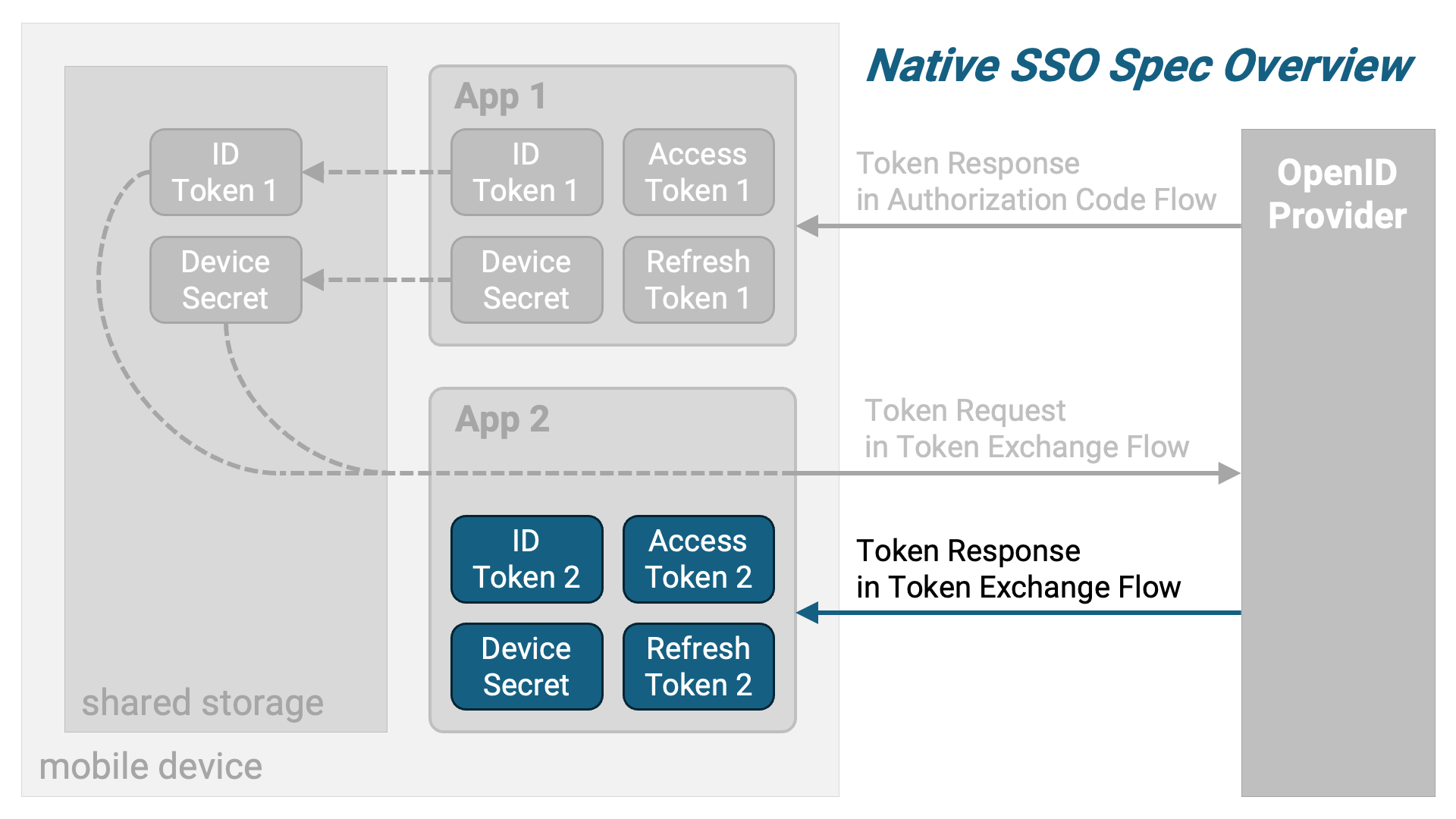
To summarize, the following diagram illustrates the overview.
The device secret is described in the Native SSO specification as follows.
The device secret contains relevant data to the device and the current users authenticated with the device. The device secret is completely opaque to the client and as such the AS MUST adequately protect the value such as using a JWE if the AS is not maintaining state on the backend.
When issuing a device secret, the OpenID Provider obtains some form of information about the device and associates it with the device secret. Then, upon receiving a token exchange request, it verifies whether the device associated with the device secret in the request matches the device from which the request was sent.
App 1 sends an authorization request based on the authorization code flow to
the OpenID Provider via a web browser. A Native SSO-specific requirement is
that the scope parameter must include both the openid scope and the
device_sso scope. The device_sso scope is defined by the Native SSO
specification.
The minimum required request parameters for an authorization request compliant with Native SSO are as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
client_id |
The client identifier, such as app_1. |
response_type |
A space-separated list of the tokens being requested. When requesting an authorization code, it includes code. |
scope |
A space-separated list of the scopes being requested. To comply with the Native SSO specification, both openid and device_sso must be included. |
redirect_uri |
The redirect URI. According to the OpenID Connect specification, the redirect_uri parameter is required when requesting the openid scope. |
Here is an example of an authorization request:
https://trial.authlete.net/api/authorization ?client_id=app_1&response_type=code&scope=openid+device_sso&redirect_uri=https://nextdev-api .authlete.net/api/mock/redirection
A token request is constructed using the authorization code obtained from the above authorization request. The request parameters required are as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
grant_type |
This is the grant type. It is a mandatory parameter regardless of the flow used. For the authorization code flow, the value should be specified as authorization_code. |
code |
This is a mandatory parameter in the authorization code flow. It specifies the authorization code obtained from the authorization request. |
redirect_uri |
This is the redirect URI. If the redirect_uri parameter was included in the preceding authorization request, it is also required in the token request. Its value must be the same as the one specified in the authorization request. |
In addition to the above, depending on the application’s client type (RFC 6749 Section 2.1), whether it is confidential or public, and which client authentication method is used in the case of a confidential client, additional parameters may be required.
For example, if the client type is public, the client_id request parameter is
mandatory. On the other hand, if the client type is confidential and the
private_ client authentication method is used, the
client_ and client_
request parameters are required. For more details on client authentication methods,
refer to
“OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication”.
The following is an example of a token request by a public client:
POST https://trial.authlete.net/api/token HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=app_1&grant_type=authorization_code&code={{authorization_code}}&redirect_uri=https://nextdev-api .authlete.net/api/mock/redirection
The token response that conforms to Native SSO includes, in addition to the
access token and refresh token (optional), an ID token and a device secret
that comply with Native SSO. The device secret is returned as the value of
the device_secret property.
{
"access_token": "R28TIqhCydVvH2x2a3XsOzJykFEs7yFotO4ip-a2MbY",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400,
"scope": "openid device_sso",
"refresh_token": "lmlNXafSApRDAq7gZvy40ojya9bplgFSHczms46mTms",
"id_token": "eyJraWQiOiJaWUdJT0hZdUE5SXBVaWpWd1FOdWwzbkU1MzZ4MUpTV0hpT2ZkUzdzYWRnIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL3RyaWFsLmF1dGhsZXRlLm5ldCIsInN1YiI6IjEwMDQiLCJhdWQiOlsiYXBwXzEiXSwiZXhwIjoxNzQ2NDM3MTE5LCJpYXQiOjE3NDYzNTA3MTksImF1dGhfdGltZSI6MTc0NjM1MDY3MiwiZHNfaGFzaCI6IlhrYmdHQ1JKUTFOQUhuS25NbjhKMFhIS25fOEVNenhCOWFRdUZITk0ycDQiLCJzaWQiOiJub2RlMDM4Y2F0N2ozMDhzZzE4MjhtMXNnMmRleGwzIn0.JAYlCEbGhjJwpgSZ4lUNaXkWD2ICeDs6FCBd3bKRvKPhrrGZKUAZDRij_Bmn_AF7DyTQS5ALHl82cJqjaLCcIw",
"device_secret": "b81d5ae9-9f85-4c6d-8658-1a36ffa42c83"
}
The value of the id_token property included in the token response is the
ID token:
eyJraWQiOiJaWUdJT0hZdUE5SXBVaWpWd1FOdWwzbkU1MzZ4MUpTV0hpT2ZkUzdzYWRnIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL3RyaWFsLmF1dGhsZXRlLm5ldCIsInN1YiI6IjEwMDQiLCJhdWQiOlsiYXBwXzEiXSwiZXhwIjoxNzQ2NDM3MTE5LCJpYXQiOjE3NDYzNTA3MTksImF1dGhfdGltZSI6MTc0NjM1MDY3MiwiZHNfaGFzaCI6IlhrYmdHQ1JKUTFOQUhuS25NbjhKMFhIS25fOEVNenhCOWFRdUZITk0ycDQiLCJzaWQiOiJub2RlMDM4Y2F0N2ozMDhzZzE4MjhtMXNnMmRleGwzIn0.JAYlCEbGhjJwpgSZ4lUNaXkWD2ICeDs6FCBd3bKRvKPhrrGZKUAZDRij_Bmn_AF7DyTQS5ALHl82cJqjaLCcIw
The payload of this ID token, when decoded using base64url, is as follows.
The ID token compliant with Native SSO specification includes the ds_hash
claim and the sid claim.
{
"iss": "https://trial.authlete.net",
"sub": "1004",
"aud": [
"app_1"
],
"exp": 1746437119,
"iat": 1746350719,
"auth_time": 1746350672,
"ds_hash": "XkbgGCRJQ1NAHnKnMn8J0XHKn_8EMzxB9aQuFHNM2p4",
"sid": "node038cat7j308sg1828m1sg2dexl3"
}
The ds_hash claim is the hash value of the device secret. How this hash value
is calculated depends on the implementation, but the ds_hash claim allows the
ID token to be associated with the device secret.
The sid claim is a string that uniquely identifies the user’s authentication
session, essentially the session ID.
App 1 stores the obtained ID token and device secret in a location accessible to other applications that are integrated with Native SSO.
The Native SSO specification extends the RFC 8693: OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange specification by adding requirements to achieve Native SSO. App 2 retrieves the ID token and device secret stored by App 1 and uses them to construct a token exchange request that complies with the Native SSO specification.
The request parameters for a token exchange request compliant with the Native SSO specification are as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
grant_type |
The grant type. In a token exchange request, specify urn:. |
audience |
The intended recipient of the token issued by the token exchange request. In a Native SSO token exchange request, specify the identifier of the OpenID Provider. |
subject_token |
The token that indicates on whose behalf the token exchange is being performed. In a Native SSO token exchange request, this is the ID token. |
subject_token_type |
The identifier indicating the type of the subject_token. In a Native SSO token exchange request, the subject_token is always an ID token, so the value must be urn:. |
actor_token |
The token that represents the actor executing the token exchange. In a Native SSO token exchange request, this is the device secret. |
actor_token_type |
The identifier indicating the type of the actor_token. In a Native SSO token exchange request, the actor_token is always a device secret, so the value must be urn:. This is a token type newly defined by the Native SSO specification. |
scope |
The scopes to associate with the access token issued as a result of the token exchange request. This parameter is optional. |
In addition to the above, depending on the application’s client type (RFC 6749 Section 2.1), whether it is confidential or public, and which client authentication method is used in the case of a confidential client, additional parameters may be required.
For example, if the client type is public, the client_id request parameter is
mandatory. On the other hand, if the client type is confidential and the
private_ client authentication method is used, the
client_ and client_
request parameters are required. For more details on client authentication methods,
refer to
“OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication”.
The following is an example of a token exchange request by a public client:
POST https://trial.authlete.net/api/token HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=app_2&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type :token-exchange &audience=https://trial.authlete.net&subject_token={{id_token}}&subject_token_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type :id_token &actor_token={{device_secret}}&actor_token_type=urn:openid:params:token-type :device-secret &scope=openid
The response to the token exchange request is almost identical to the token
response of the authorization code flow. The only difference is that it
includes the issued_ property. In the case
of Native SSO, the value of issued_ is
urn:.
{
"access_token": "rH9115-g83z9zIiCJ1mzIe8mza3bX4NaBTWmGs5qqow",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400,
"scope": "openid",
"refresh_token": "_F7NMCU1ny8DQ-3Pru_owgII52gIew0T6wuWKeIrfL4",
"id_token": "eyJraWQiOiJaWUdJT0hZdUE5SXBVaWpWd1FOdWwzbkU1MzZ4MUpTV0hpT2ZkUzdzYWRnIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL3RyaWFsLmF1dGhsZXRlLm5ldCIsInN1YiI6IjEwMDQiLCJhdWQiOlsiYXBwXzIiXSwiZXhwIjoxNzQ2NDM4MzUxLCJpYXQiOjE3NDYzNTE5NTEsImRzX2hhc2giOiJYa2JnR0NSSlExTkFIbktuTW44SjBYSEtuXzhFTXp4QjlhUXVGSE5NMnA0Iiwic2lkIjoibm9kZTAzOGNhdDdqMzA4c2cxODI4bTFzZzJkZXhsMyJ9.8jNNF5mpeHnbqp1FTK_1adR8FlgPmHK9_rwUzaz-o5P7RMyaelBaSj74IhxHY6wbCJeD0n_N14h8vD8zWYh-8w",
"device_secret": "b81d5ae9-9f85-4c6d-8658-1a36ffa42c83",
"issued_token_type": "urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:access_token"
}
Extracting the ID token from the above response example:
eyJraWQiOiJaWUdJT0hZdUE5SXBVaWpWd1FOdWwzbkU1MzZ4MUpTV0hpT2ZkUzdzYWRnIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL3RyaWFsLmF1dGhsZXRlLm5ldCIsInN1YiI6IjEwMDQiLCJhdWQiOlsiYXBwXzIiXSwiZXhwIjoxNzQ2NDM4MzUxLCJpYXQiOjE3NDYzNTE5NTEsImRzX2hhc2giOiJYa2JnR0NSSlExTkFIbktuTW44SjBYSEtuXzhFTXp4QjlhUXVGSE5NMnA0Iiwic2lkIjoibm9kZTAzOGNhdDdqMzA4c2cxODI4bTFzZzJkZXhsMyJ9.8jNNF5mpeHnbqp1FTK_1adR8FlgPmHK9_rwUzaz-o5P7RMyaelBaSj74IhxHY6wbCJeD0n_N14h8vD8zWYh-8w
and decoding its payload part using base64url will show this result:
{
"iss": "https://trial.authlete.net",
"sub": "1004",
"aud": [
"app_2"
],
"exp": 1746438351,
"iat": 1746351951,
"ds_hash": "XkbgGCRJQ1NAHnKnMn8J0XHKn_8EMzxB9aQuFHNM2p4",
"sid": "node038cat7j308sg1828m1sg2dexl3"
}
The values of the ds_hash and sid claims are the same as those in the ID
token received by App 1, but the value of the aud claim is different. In this
ID token, the identifier of App 2, app_2, is included in the aud array.
Authlete supports Native SSO starting from version 3.0.
A new boolean property, nativeSsoSupported, has been added to the service to
indicate whether Native SSO is supported. The default value of this property is
false, so if you want to enable Native SSO, you must explicitly set it to true.
The nativeSsoSupported property corresponds to the
native_ server metadata defined by the
Native SSO specification. When native is set
to true, the discovery document generated by Authlete’s
/service API (as defined in
OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0)
will include the following entry:
"native_sso_supported": true
If nativeSsoSupported is set to false, Authlete behaves as if it has no
knowledge of Native SSO. For example, the device_sso scope no longer has any
special meaning, and the token type
urn:
is treated as an unknown token type (which results in an error if specified as
the value of actor_).
For Native SSO, the authorization server must support the device_sso scope.
Be sure to explicitly register the device_sso scope.
Due to requirements in the OAuth 2.0 specification, an authorization server
does not treat unknown scopes as errors; it simply ignores them. As a result,
if the device_sso scope is not registered, including it in an authorization
request will not trigger any warning, and processing specific to Native SSO
will silently be skipped.
Please add TOKEN_EXCHANGE to the list of supported grant types of the service.
Additionally, Authlete has several configuration items related to Token Exchange, so please verify that they are set correctly. Pay special attention to the following two items:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
token |
This boolean property indicates whether token exchange requests are limited to confidential clients only. If set to true, token exchange requests from public clients will not be accepted. |
token |
This boolean property indicates whether token exchange requests are restricted to pre-approved clients. If set to true, token exchange requests from clients that have not been explicitly authorized will not be accepted. |
To configure Native SSO in the Authlete Management Console:
Service Settings > Tokens and Claims > Advanced > Token ExchangeNative SSO section and toggle Allow to enable.Save Changes to apply the update.
To register the device_sso scope:
Service Settings > Tokens and Claims > Advanced > ScopeSupported Scopes and click the Add button.device_sso for the scope name and click add.Save Changes to apply the update.
To add the Token_Exchange Grant Type:
Service Settings > Endpoints > Global Settings > GeneralSupported Grant Types, and select the Token_Exchange option.Save Changes to apply the update.
Note: When using the
Token_ExchangeGrant Type, make sure to enable additional settings in the client. Go toclient settings > Tokens and claims > Advanced > Token Exchangeand enable theExplicit Permission for Token Exchangeoption.

Depending on the settings, the scopes that a client can request may be
restricted. In such cases, ensure that the device_sso scope is added
to the list of allowed scopes that can be requested.
Add TOKEN_EXCHANGE to the list of grant types that the client can use.
Also, if the service’s token
property is set to true, token exchange requests from clients that are not
explicitly permitted will be rejected. In such cases, you need to set the
extension. property of
the client to true in the client’s settings.
To add the Token_Exchange Grant Type:
Client Settings > Endpoints > Global Settings > GeneralSupported Grant Types, and select the Token_Exchange option.Save Changes to apply the update.
To register the device_sso scope:
Client Settings > Tokens and Claims > Advanced > ScopeAdd Requestable scope and enter device_ssofor the scope name.Save Changes to apply the update.
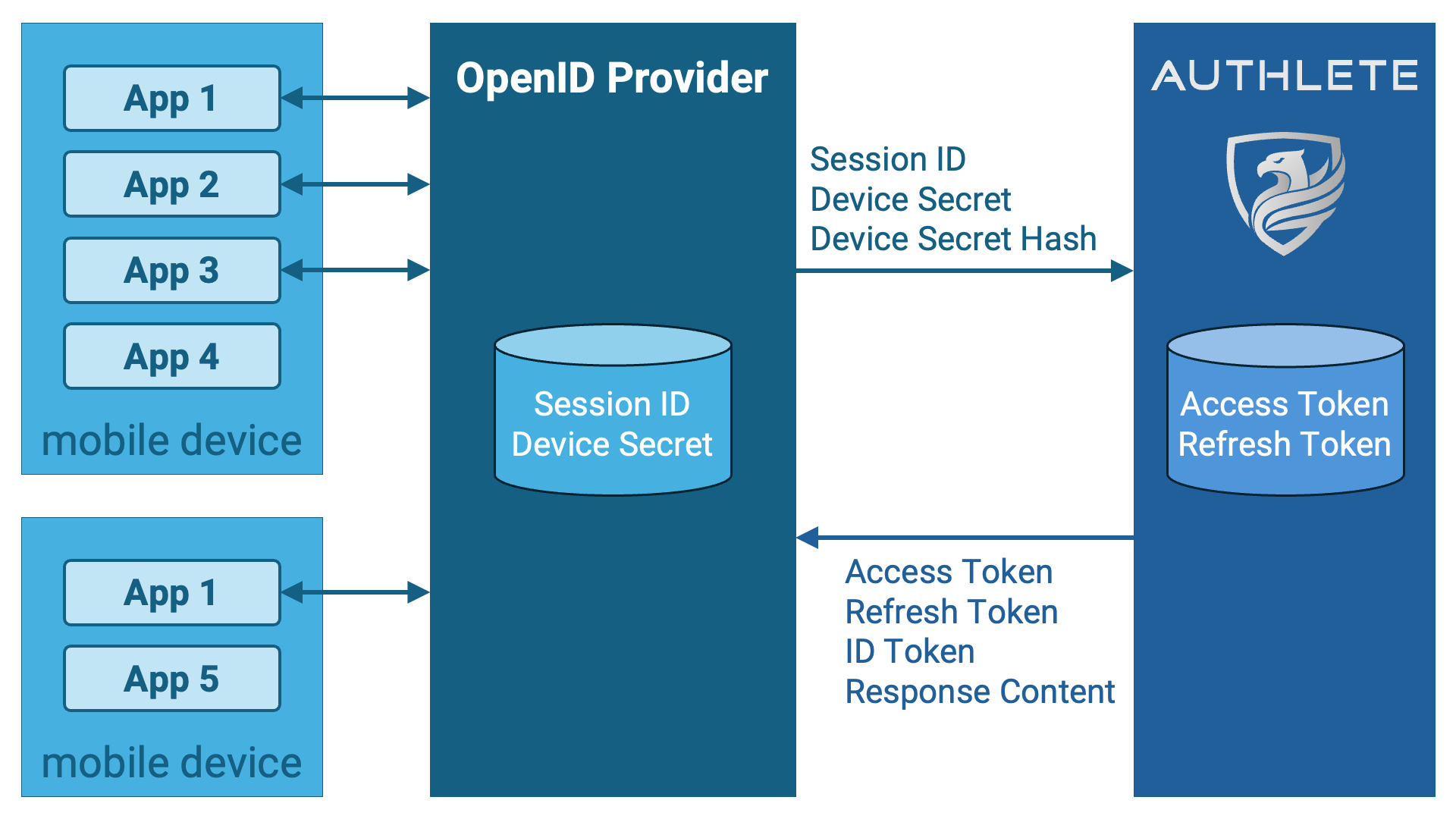
A key feature of Authlete is the complete separation of user authentication and management from OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect protocol processing, focusing only on the latter, which has gained significant market support. Due to this unique architecture, Authlete does not manage user authentication sessions. Consequently, the management of authentication sessions is the responsibility of the Authlete users (OpenID Provider implementers).
For ID tokens conforming to Native SSO, the session ID value must be embedded
as the sid claim, and this value will be managed by the OpenID Provider.
Another characteristic of the Authlete architecture is that it operates in the backend and does not communicate directly with client applications. As a result, Authlete cannot directly access information about the device on which the client application is running. The OpenID Provider conforming to Native SSO must issue a device secret associated with the device information, but Authlete cannot do this. The generation and management of device secrets are also the responsibility of the OpenID Provider.
On the other hand, Authlete generates ID tokens and token responses conforming to Native SSO. The necessary session ID, device secret (and device secret hash) for generating these must be passed from the OpenID Provider to Authlete through the request parameters of Authlete APIs.
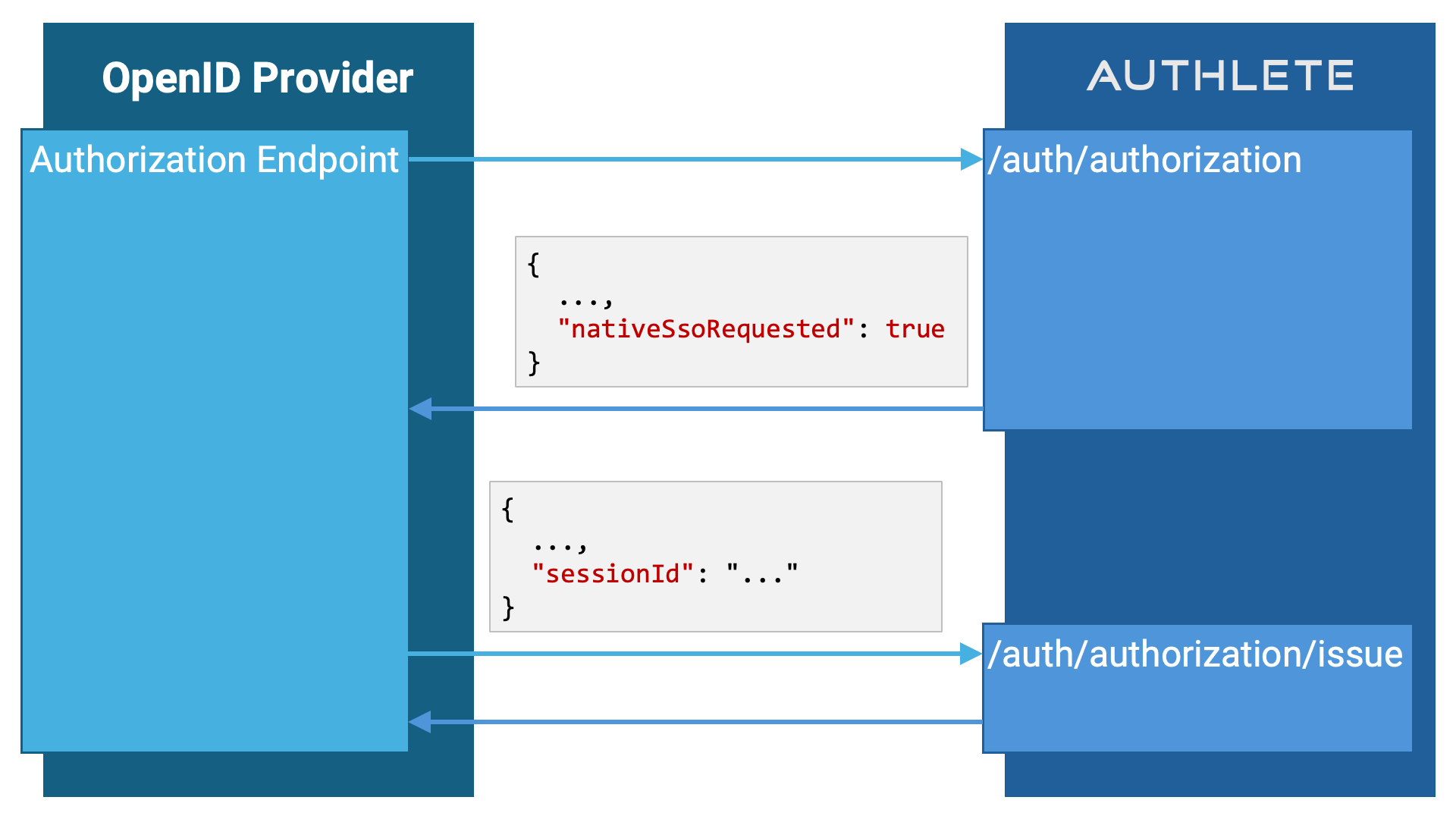
When an authorization request is determined to be requesting Native SSO,
specifically when all of the following conditions are met, the response from
Authlete’s /auth API will include a boolean
property native with the value true.
| Condition | |
|---|---|
| 1 | The service supports Native SSO. (The value of Service. is set to true.) |
| 2 | The service supports the openid and device_sso scopes. |
| 3 | The client is permitted to request the openid and device_sso scopes. (The client is not restricted by the Requestable Scopes feature.) |
| 4 | The scope of the authorization request includes both openid and device_sso. |
| 5 | The service supports the authorization code flow. (Service. includes AUTHORIZATION_.) |
| 6 | The client declares that it uses the authorization code flow. (Client. includes AUTHORIZATION_.) |
| 7 | The response_type of the authorization request includes code. |
| 8 | The service supports this response type. (Service. includes the corresponding response type.) |
| 9 | The client declares that it uses this response type. (Client. includes the corresponding response type.) |
The conditions in this table may seem complex, but if we focus only on the
conditions of the authorization request, excluding the service and client
settings, it can be simplified: “If the scope includes openid and
device_sso and the response_type includes code”, it is considered
a request for Native SSO.
When the value of the nativeSsoRequested property is true, the
implementation of the authorization endpoint must include the sessionId
request parameter when calling the /auth
API. The value should represent an identifier for the current user’s
authentication session (i.e., the session ID). The value provided here will
be used as the value for the sid claim in the ID token.
The implementation of the authorization endpoint may pass the actual session
ID value as the sessionId parameter to Authlete, or it may pass a transformed
version of it. However, the string should not be too long. Generally, the upper
limit is around 150 characters. If the length of the string resulting from
encrypting the sessionId and base64url encoding it exceeds 255 characters, an
error will occur (the encryption logic is not publicly disclosed).
It is also acceptable to always pass the sessionId parameter to the
/auth API, regardless of whether the
value of native in the
/auth API response is true or false. If the
authorization request does not request Native SSO, even if the sessionId
parameter is provided, Authlete will not embed the sid claim in the ID token.
If a token request is determined to be for Native SSO — specifically, if one of
the following sets of conditions is satisfied — then the value of the action
property in the response from Authlete’s /auth API will
be NATIVE_.
| Conditions Set 1: Authorization Code Flow | |
|---|---|
| 1 | The service supports Native SSO. (The value of Service. is set to true.) |
| 2 | The service supports the openid and device_sso scopes. |
| 3 | The client is allowed to request the openid and device_sso scopes. (The client is not restricted by the Requestable Scopes feature.) |
| 4 | The corresponding authorization request’s scope contains both openid and device_sso. |
| 5 | The service supports the authorization code flow. (Service. includes AUTHORIZATION_.) |
| 6 | The client declares the use of the authorization code flow. (Client. includes AUTHORIZATION_.) |
| 7 | The value of the grant_ parameter is authorization_. |
| Conditions Set 2: Refresh Token Flow | |
|---|---|
| 1 | The service supports Native SSO. (The value of Service. is set to true.) |
| 2 | The service supports the device_sso scope. |
| 3 | The client is allowed to request the device_sso scope. (The client is not restricted by the Requestable Scopes feature.) |
| 4 | The service supports the refresh token flow. (Service. includes REFRESH_.) |
| 5 | The client declares the use of the refresh token flow. (Client. includes REFRESH_.) |
| 6 | The value of the grant_ parameter is refresh_. |
| 7 | Even if the scope range is narrowed by the scope parameter in the token request, the device_sso scope is still covered. |
| 8 | The presented refresh token is associated with the user authentication session. (Effectively, only refresh tokens generated by an authorization code flow compliant with Native SSO can be used.) |
| Conditions Set 3: Token Exchange Flow | |
|---|---|
| 1 | The service supports Native SSO. (The value of Service. is set to true.) |
| 2 | The service supports the token exchange flow. (Service. includes TOKEN_.) |
| 3 | The client declares the use of the token exchange flow. (Client. includes TOKEN_.) |
| 4 | Various settings for the service’s token exchange flow (e.g., token) do not reject the client’s token exchange request. |
| 5 | The value of the grant_ parameter is urn:. |
| 6 | The value of the actor_ parameter is urn:. |
The conditions listed above may seem complex, but essentially, if Authlete
determines that it needs to generate an ID token and token response compliant
with Native SSO, the value of action will be NATIVE_SSO.
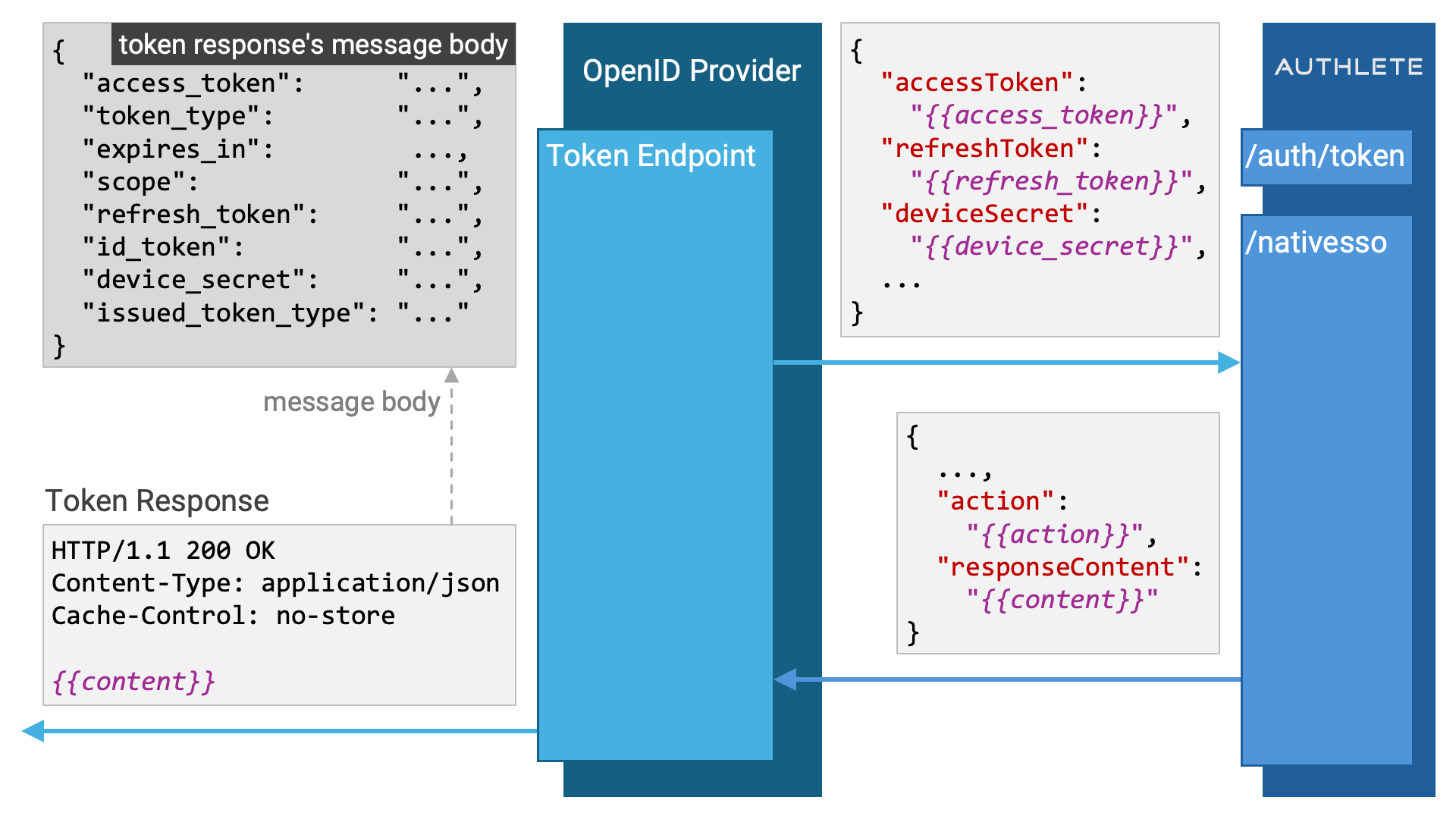
When the action is set to NATIVE_SSO, the implementation of the token
endpoint must call the /nativesso API to complete the token request process.
However, prior to that, it must validate the session ID and device secret and,
if necessary, generate the device secret.
If the /auth/token API response includes an additionalClaims field containing a JSON string with the nonce and s_hash claims, pass that value directly to the /nativesso API via the claims parameter:
{
"accessToken": "{{accessToken}}",
"deviceSecret": "{{deviceSecret}}",
"claims": "{{additionalClaims}}"
}
When additionalClaims is provided, the claims parameter must contain that exact JSON string. These claims are essential for ID token validation and will be embedded in the generated ID token by the /nativesso API.
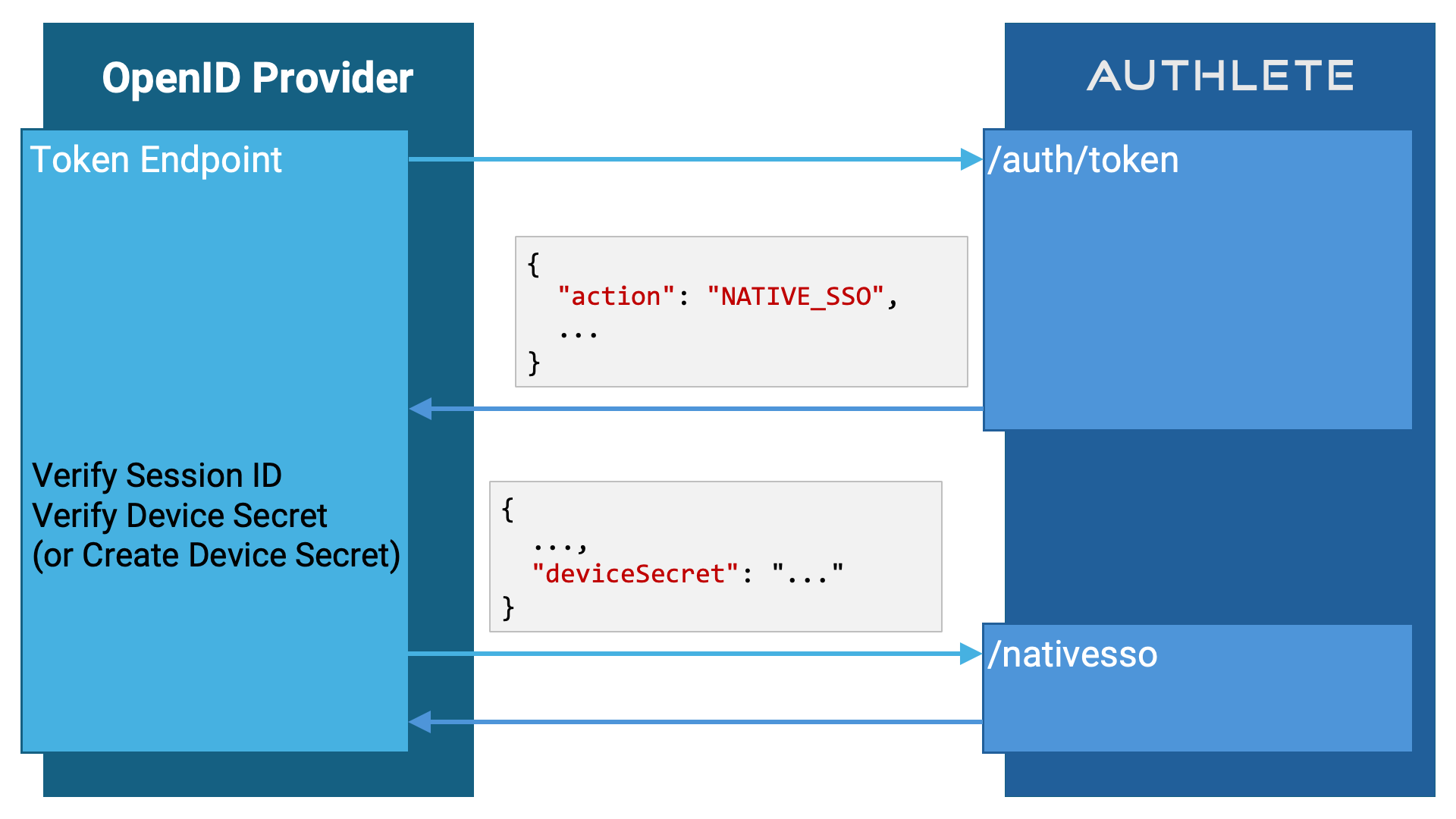
When the value of action in the response from the /auth
API is NATIVE_SSO, the response will include a sessionId parameter, which
represents the user’s authentication session, i.e., the session ID. The token
endpoint implementation must verify whether this session ID is still valid.
If it is invalid, the implementation should not call the /nativesso API.
Instead, it should generate a token response indicating the invalid_grant
error and return it to the client.
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
{
"error": "invalid_grant",
"error_description": "The session ID is no longer valid."
}
The sessionId value in the response from the /auth/token API is originally
passed from the OpenID Provider to Authlete as the sessionId request parameter
in the /auth API. Authlete does not
determine whether the session ID is valid (since it cannot), so the validation
of the session ID must be performed by the OpenID Provider.
If the token request is for the authorization code flow or refresh token flow,
the sessionId value is the session ID associated with the authorization code
or refresh token.
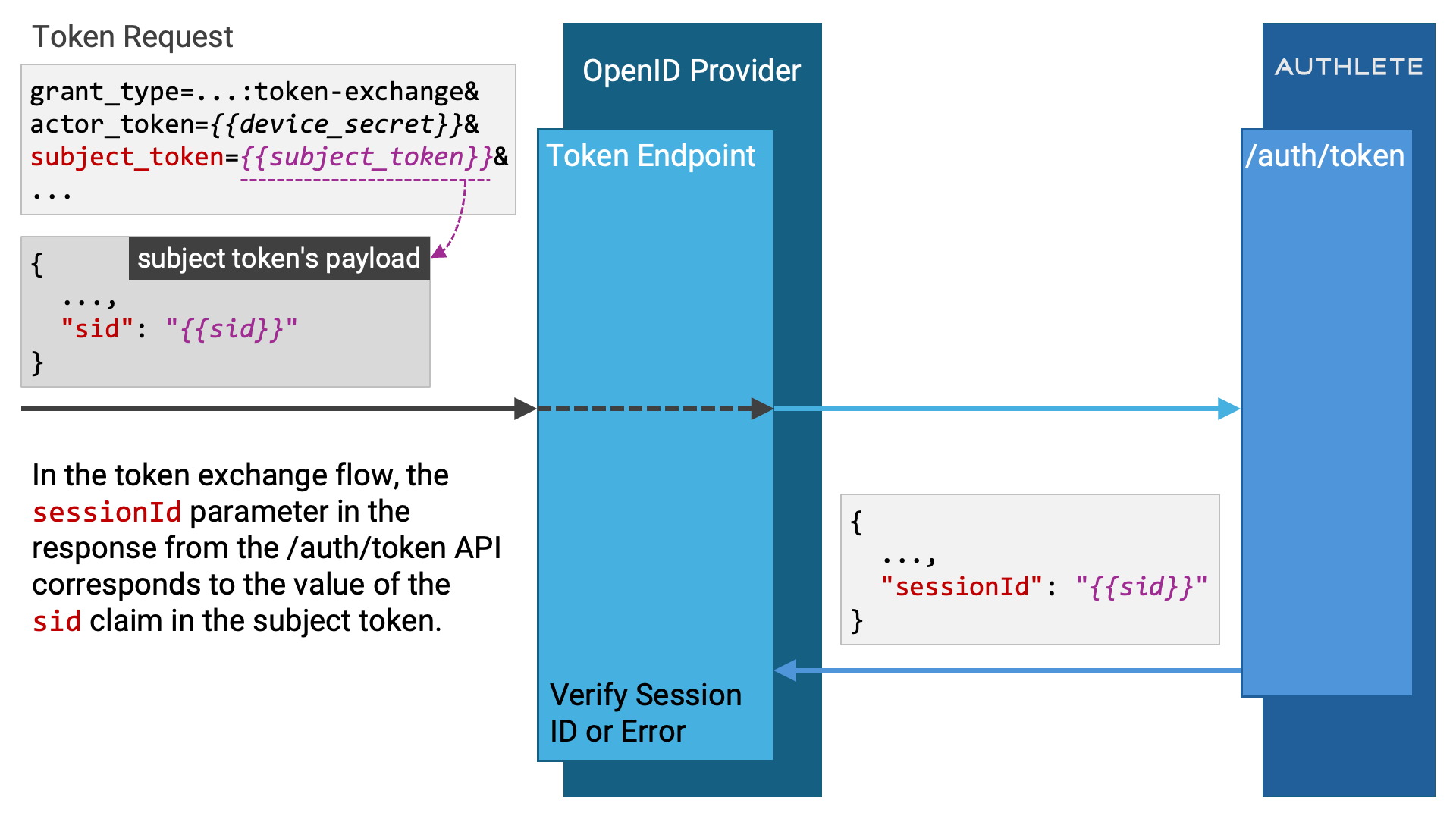
In the case of a token request for token exchange, the sessionId value is the
sid claim value from the ID token presented as the
subject_ parameter.
When the action value is NATIVE_SSO and the token request is for either the
authorization code flow or refresh token flow (i.e., when the grantType is
AUTHORIZATION_ or REFRESH_), the
response from the /auth API may include the
device parameter.
The value of this parameter will be the value of the device_
request parameter from the token request. However, note that this
device_ request parameter is optional, meaning that it
may or may not be included in the request.
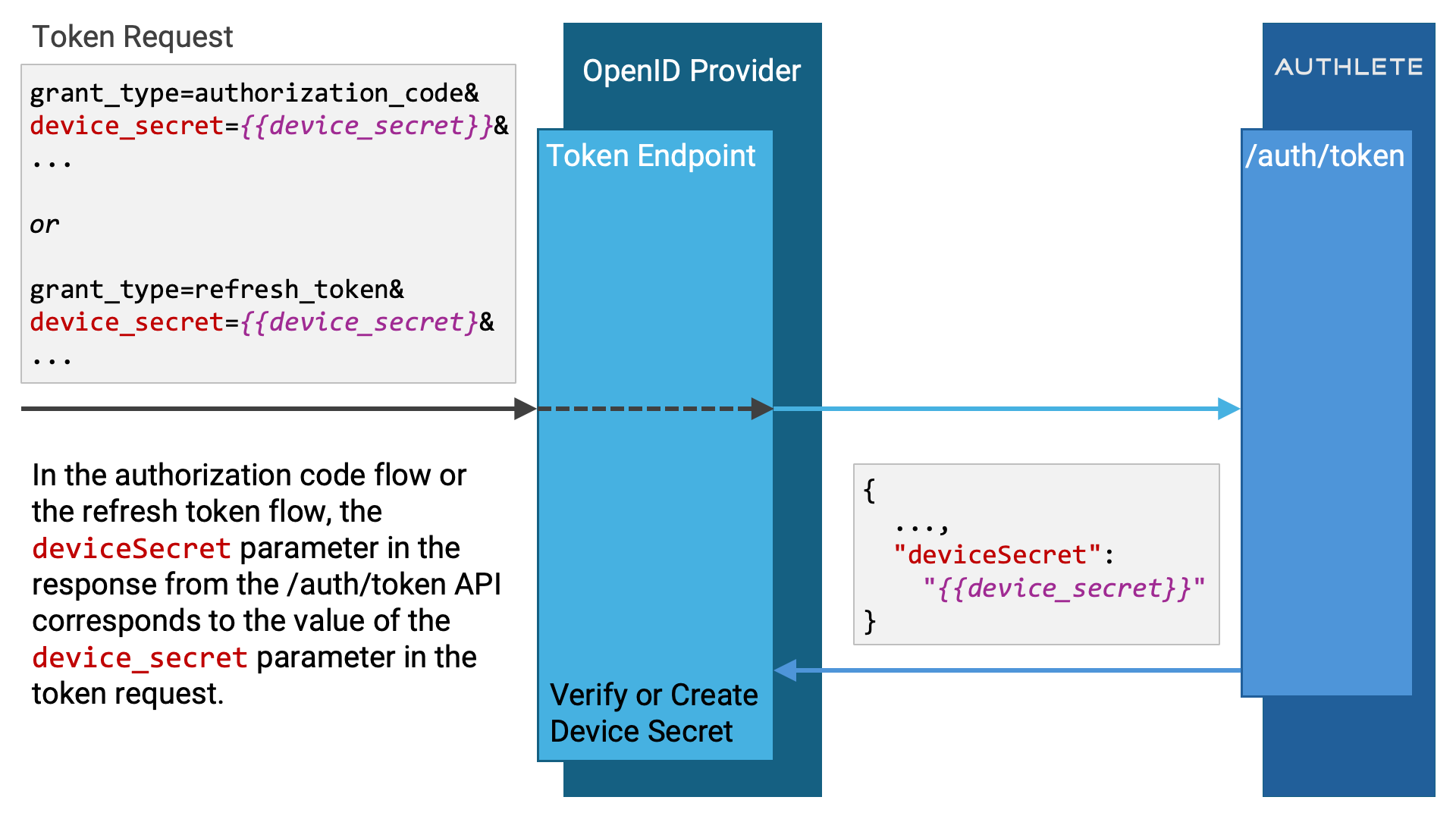
If the value of device is not null, it must be
verified. If it is valid, the same value should be passed to the /nativesso
API later.
If the value of device is either missing or invalid,
a new device secret must be generated and that value must be passed to the
/nativesso API.
When the action value is NATIVE_SSO and the token request is for a token
exchange flow (i.e., grantType is TOKEN_), the
response from the /auth API will always include both
the device and device
parameters.
The device value corresponds to the device secret
specified in the actor_ parameter of the token request.
The device value corresponds to the ds_hash
claim included in the ID token specified in the subject_
parameter of the token request.
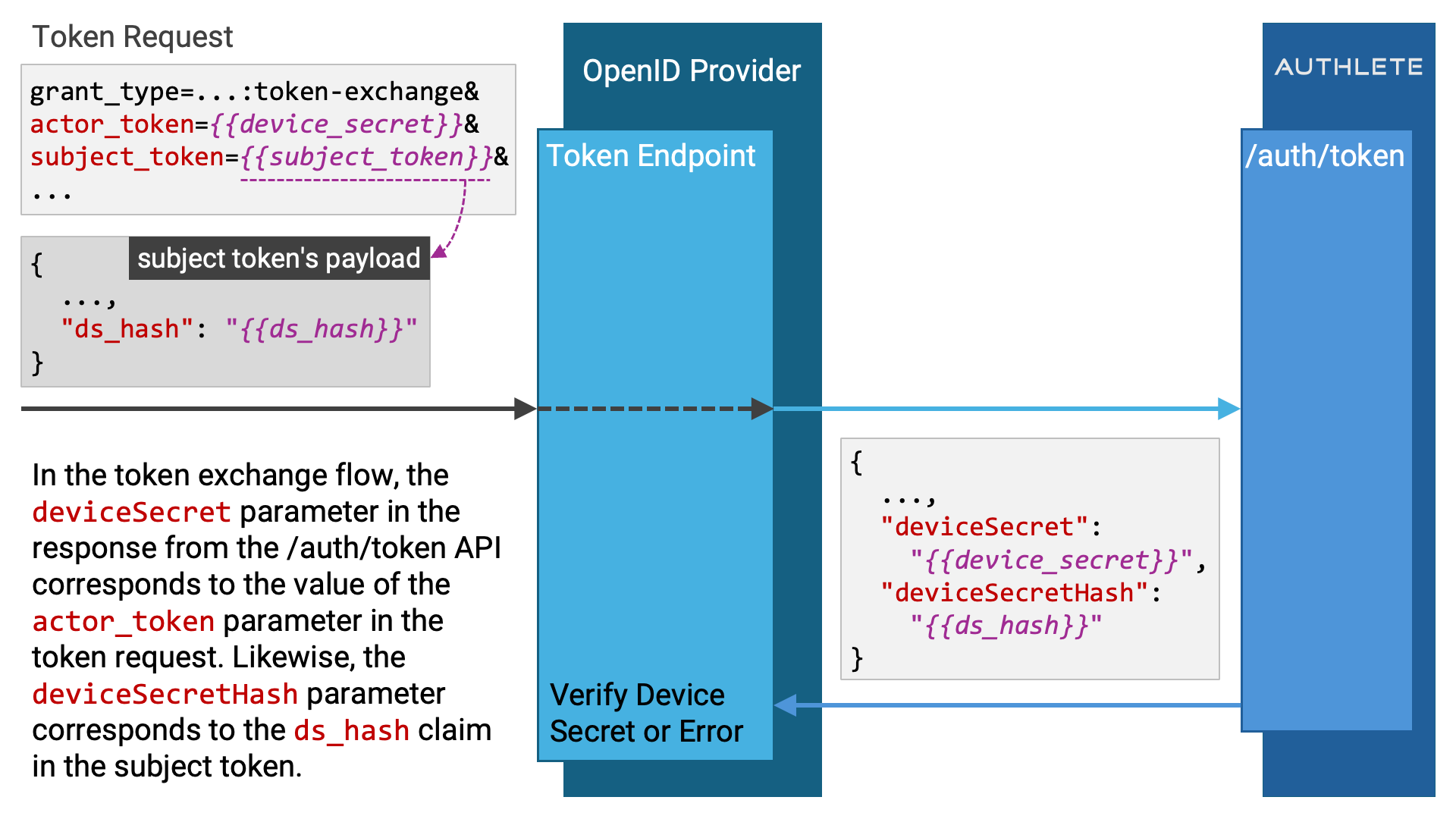
In the token endpoint implementation, the device secret hash must be verified
to ensure it corresponds to the correct device secret. If it does not match,
the /nativesso API should not be called. Instead, a token response indicating
the invalid_grant error should be generated and returned to the client.
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
{
"error": "invalid_grant",
"error_description": "The device secret hash in the subject token does not correspond to the device secret."
}
After the verification of the session ID and the verification or generation of
the device secret, the /nativesso API should be called to generate the ID
token and token response that comply with Native SSO.
The /nativesso API accepts HTTP POST requests in either
application/ or
application/ formats.
The request parameters are as follows:
| Parameter | Necessity | Description |
|---|---|---|
access |
Required | If the jwt is included in the /auth API response, specify its value. If not, specify the value of access. The provided value will be used as the access_ property in the token response prepared by the /nativesso API. |
refresh |
Optional | Specify the value of refresh included in the /auth API response. The specified value will be used as the refresh_ property in the token response prepared by the /nativesso API. |
device |
Required | If the device is included in the /auth API response, specify its value. If not, generate a new device secret and specify its value. The provided value will be used as the device_ property in the token response prepared by the /nativesso API. |
device |
Recommended | Specify the hash value of the device secret. The logic to derive the hash value from the device secret depends on the implementation of the OpenID Provider. If this parameter is omitted, the implementation of the /nativesso API will compute the SHA-256 hash of the device value and use the base64url encoded version of the hash as the device secret hash. The value specified in the device parameter, or the value generated by the /nativesso API, will be embedded as the ds_hash claim in the ID token generated by the /nativesso API. |
sub |
Optional | This is the sub claim value of the ID token generated by the /nativesso API. If this parameter is omitted, the subject linked to the access token specified in the access parameter will be used as the sub claim value.Since Authlete APIs that generate ID tokens accept a sub request parameter, the /nativesso API also accepts this parameter. However, using a different value from the subject of the access token as the sub claim may cause unintended inconsistencies, so please use this sub parameter carefully.Regardless of the value of this sub parameter, when generating a new access token in the Native SSO token exchange flow, Authlete will set the sub claim from the subject token (the ID token generated from a previous /nativesso API call) as the subject of the new access token. Once the /auth API has returned the response, the access token has already been created, and the sub parameter in the /nativesso API cannot change the subject of the access token. |
claims |
Optional | Specify claims to be embedded in the ID token. The value must be a JSON object represented as a string. For Native SSO, this parameter serves two purposes: 1. Propagating required protocol claims: When the /auth/token API response includes an additionalClaims field (containing nonce and s_hash), its value must be passed unchanged to the claims parameter. These claims are required for ID token validation.2. Adding custom claims: If the implementation needs to embed additional custom claims, merge them with the additionalClaims JSON before sending it in this parameter.In summary: - If additionalClaims is present and no custom claims are needed, set claims to that value directly.- If additionalClaims is present and custom claims are also needed, merge both JSON objects and send the result as claims parameter.- If additionalClaims is not returned and no custom claims are needed, you can omit the claims parameter or send an empty JSON object.- If additionalClaims is not returned but you need to add custom claims, set claims to the custom claims JSON. |
idt |
Optional | Specify additional parameters to be embedded in the JWS header of the ID token. The format must be a string representing a JSON object. |
id |
Optional | Specify the format of the aud claim in the ID token. If array is specified, the value of the aud claim will be a JSON array. If string is specified, the value will be a JSON string. If this id parameter is omitted, the id property of the service will be referenced. If this property is not set in the service, the value of the aud claim will be a JSON array. |
The response message body from the /nativesso API is in JSON format. As with
many other Authlete APIs, the /nativesso API response also includes an
action property. The token endpoint implementation constructs the token
response according to the value of this action.
When the action is OK, it indicates that the /nativesso API processing
has successfully completed. In this case, the token endpoint implementation
should return a successful response (200 OK) to the client. The value of
the responseContent property in the /nativesso API response can be used
directly as the message body of the token response. Therefore, the success
response can be constructed as follows:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
(Embed the value of responseContent here.)
When the action is INTERNAL_, it indicates
that something has gone wrong on the Authlete side. For example, an issue such
as a database error might have occurred when retrieving the access token
specified by the access parameter from the database.
In such cases, the token endpoint implementation should return an error
response to the client. The simplest implementation would be to return a
500 Internal Server Error.
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
(Embed the value of responseContent here.)
However, in a production environment, it may be better to return a more abstract
error (one that does not directly describe the nature of the issue), rather
than a 500 error.
When the action is CALLER_ERROR, it indicates that the issue lies with the
caller of the API (i.e., the implementation of the OpenID Provider).
For example, this could be due to missing a required parameter such as
access.
If CALLER_ERROR is returned, please review the implementation of your OpenID
Provider.
The process of logging out from multiple applications in a single operation is called Single Logout (SLO). It complements Single Sign-On (SSO).
The Native SSO specification does not define a specific protocol to achieve Single Logout. However, Single Logout can be realized by collectively deleting the access tokens and refresh tokens associated with a particular session ID.
Authlete provides a Single Logout feature via the /nativesso
API. This API accepts HTTP POST requests in either application/
or application/ format.
It takes a single request parameter: sessionId.
When the /nativesso API is called with the target
session ID specified in the sessionId parameter, all access tokens and
refresh tokens associated with that session ID will be deleted.
POST https://{{authlete_api_server}}/api/{{service_id}}/nativesso/logout HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer {{authlete_access_token}}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"sessionId": "{{session_id}}"
}
{
"action": "OK",
"count": 2,
"resultCode": "A503001",
"resultMessage": "[A503001] The /nativesso/logout API call successfully deleted 2 access/refresh token record(s)."
}
Even if there are no access tokens or refresh tokens associated with the
specified session ID — and as a result, the number of deleted tokens is
zero — the /nativesso API does not return an error.
{
"action": "OK",
"count": 0,
"resultCode": "A503002",
"resultMessage": "[A503002] The /nativesso/logout API call completed without deleting any access/refresh token records."
}
The sample implementation of Native SSO on the OpenID Provider side is included in the java-oauth-server and authlete-java-jaxrs library. Both are open-source implementations written in Java.
Below are some tips for reading through the sample implementation:
/auth/authorization/issue API is obtained in the AuthorizationHttpServletRequest.getSession(false).getId() . However, since this session is the HTTP session between the web server and browser, a different mechanism would likely be used in a production-ready Native SSO implementation./auth/authorization/issue API through the callAuthorizationIssue method of Authleteaction in the /auth/token API response is written in the Tokenaction is NATIVE_SSO, TokennativeSso method of the Tokenprocess method of the NativenativeSso method./auth/token API.retrieveDeviceId() method. Note: in the sample implementation, this method is empty.validateParameters method in NativeisActiveSessionId(String) method of the SessionAuthlete supports Native SSO starting from version 3.0.
The first version of Authlete Native SSO was implemented based on draft 07 of
OpenID Connect Native SSO for Mobile Apps 1.0
specification. Therefore, urn:
identifiers are used instead of urn:
identifiers, which were used in earlier drafts.
If the token exchange request contains the actor_
parameter, and its value is
urn:,
Authlete will perform the following validation for the request parameters
specific to the token exchange request. Only if all validations pass, will
the action in the /auth API response be
NATIVE_.
audience parameter is specified and its value matches the service’s OpenID Provider identifier (the value set in Service.issuer ). Note that multiple audience values can be specified, and as long as one of them matches, it is sufficient.requested_token_type parameter is specified, and its value is a known token type.subject_token_type parameter is specified, and its value is urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type :id_token .subject_token parameter is specified, and its value (ID token) passes all the following validation checks:
exp claim, and its value is numeric. Note: In the context of Native SSO, it is not checked that the exp value is in the future relative to the current time. This means that an expired ID token can be specified as a subject token. (see: id_token usage)iat claim, and its value indicates the current time or a time in the past.nbf claim is included, its value indicates the current time or a time in the past.iss claim, and its value matches the service’s OpenID Provider identifier (the value set in Service.issuer ).sub claim, and its value is a string.aud claim, and its value is either a string or an array. If an array is used, it must contain at least one element, and all elements must be strings.nonce claim is included, its value is a string.sid claim, and its value is a string.ds_hash claim, and its value is a string.actor_token parameter is specified.