Table of Contents
Authlete has a feature that can issue JWT-formatted access tokens. This article describes how to enable the feature, and how to specify additional claims to an access token.
This feature is available in Authlete 2.1 and later.
Register a JWK set document to “JWK Set Content” section in Service Settings. See the following article for instructions.
After the registration, choose an appropriate “Access Token Signature Algorithm” in the same “Token” tab. For example, you would choose “ES256” if you have registered an ES256 signing key (shown in the article above).
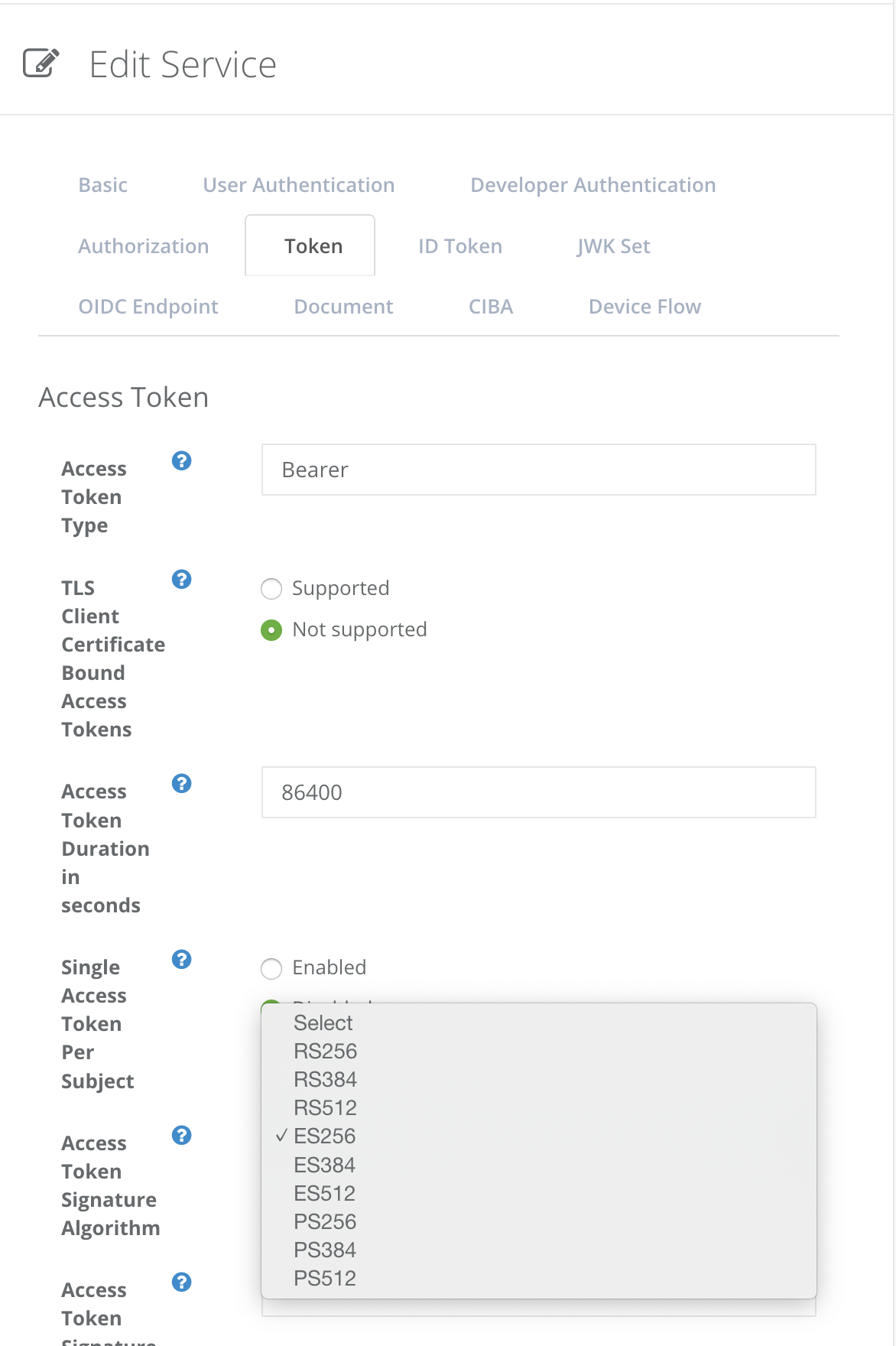
After the change, access tokens to be issued by Authlete are JWT-formatted.
You can embed arbitrary key-value pairs into access tokens in either of the following ways:
The following sections describe the overview.
The jwtAtClaims parameter is available in Authlete 2.3 or later.
The “Extra Properties ” feature allows an authorization server to associate arbitrary properties with either an access token or an authorization code. By using this feature for the JWT-formatted access tokens, visible (= not-hidden) extra properties are included in the access tokens as custom claims so that resource servers can extract them.
The following is an execution example of /auth/token API of the Authlete service configured to issue JWT-formatted access tokens. This example also shows output when using extra properties.
You will see a JWS signed JWT as a value of “access_token” in “responseContent” (content of token response). The same value is also provided as “jwtAccessToken”. (folded for readability)
POST https://eaxample.authlete.com/api/auth/token
Authorization: {{API_Key/API_SECRET}}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"clientId":"...",
"clientSecret":"...",
"parameters":
"grant_type=authorization_code&
redirect_uri=https://client.example.org/cb/example.com&
code=..."
}
{
"type": "tokenResponse",
"resultCode": "A050001",
"resultMessage": "[A050001] The token request (grant_type=authorization_code) was processed successfully.",
"accessToken": "xx2...AFQ",
"accessTokenDuration": 86400,
"accessTokenExpiresAt": 1591690046802,
"action": "OK",
"clientId": 17201083166161,
"clientIdAliasUsed": false,
"grantType": "AUTHORIZATION_CODE",
"jwtAccessToken": "eyJraWQiOiIxIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ. \
eyJleGFtcGxlX3BhcmFtZXRlciI6ImV4YW1wbGVfdmFsdWUiLCJz \
dWIiOiJ0ZXN0dXNlcjAxIiwic2NvcGUiOm51bGwsImlzcyI6Imh0 \
dHBzOi8vYXV0aGxldGUuY29tIiwiZXhwIjoxNTkxNjkwMDQ2LCJp \
YXQiOjE1OTE2MDM2NDYsImNsaWVudF9pZCI6IjE3MjAxMDgzMTY2 \
MTYxIiwianRpIjoieHgycnNJODBER1Z4bHFLdTFQV2R4eWJSLTdB \
eTZWamJNcTAxY3dNYkFGUSJ9. \
-9RsKUSnJHmdqNtNpWbbbTah1YxTkicsabIgxrLWHtGiLsTIaEj_ \
q39AvKYWrmfnw5y0dfaD3qtTScxI94OSIg",
"properties": [
{
"hidden": false,
"key": "example_parameter",
"value": "example_value"
}
],
"refreshToken": "4rA7H1uRZkCQ7Yd0PN98h7IUqW7zT8p1a_BAg0jEyow",
"refreshTokenDuration": 864000,
"refreshTokenExpiresAt": 1592467646802,
"responseContent": "{"access_token": "eyJraWQiOiIxIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ. \
eyJleGFtcGxlX3BhcmFtZXRlciI6ImV4YW1wbGVfdmFsdWUiLCJz \
dWIiOiJ0ZXN0dXNlcjAxIiwic2NvcGUiOm51bGwsImlzcyI6Imh0 \
dHBzOi8vYXV0aGxldGUuY29tIiwiZXhwIjoxNTkxNjkwMDQ2LCJp \
YXQiOjE1OTE2MDM2NDYsImNsaWVudF9pZCI6IjE3MjAxMDgzMTY2 \
MTYxIiwianRpIjoieHgycnNJODBER1Z4bHFLdTFQV2R4eWJSLTdB \
eTZWamJNcTAxY3dNYkFGUSJ9. \
-9RsKUSnJHmdqNtNpWbbbTah1YxTkicsabIgxrLWHtGiLsTIaEj_ \
q39AvKYWrmfnw5y0dfaD3qtTScxI94OSIg", \
"refresh_token":"4rA7H1uRZkCQ7Yd0PN98h7IUqW7zT8p1a_BAg0jEyow",
"example_parameter": "example_value",
"scope": null,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400}",
"subject": "testuser01"
}
Header and payload of the JWT access token are as follows. The latter includes the extra properties ("example_parameter":"example_value" ).
{
"kid": "1",
"alg": "ES256"
}
{
"example_parameter": "example_value",
"sub": "testuser01",
"scope": null,
"iss": "https://authlete.com",
"exp": 1591690046,
"iat": 1591603646,
"client_id": "17201083166161",
"jti": "xx2rsI80DGVxlqKu1PWdxybR-7Ay6VjbMq01cwMbAFQ"
}
The jwtAtClaims request parameter allows you to add JSON objects as claims to a JWT access token. This parameter is available when making a request to the following Authlete APIs.
The format of the value specified for jwtAtClaims is a JSON object. The properties in the JSON object specified in jwtAtClaims will be added to the JWT access token payload.
Below is an example using jwtAtClaims as one of the parameters of the request to the /auth/authorization/issue API.
POST https://eaxample.authlete.com/api/auth/authorization/issue
Authorization: {{API_Key/API_SECRET}}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"ticket": "{{ticket}}",
"subject": "abc",
"jwtAtClaims": "{\"realm\_access\": {\"roles\":[\"A\", \"B\"]}}"
...
}
The resulting JWT access token looks like this:
{
"sub": "abc",
"iss": "https://example.authlete.com",
"realm_access": {
"roles": [
"A",
"B"
]
},
...
}
When the Authlete token issuance endpoint successfully issues an access token, in addition to the responseContent that is returned to the authorization server, the following properties are also included in the response:
accessTokenjwtAccessToken (if configured to issue a JWT-based token, this is identical to the access_token in the responseContent)The authorization server can freely construct its own token response using the above response. For example, it could add a custom property containing an identifier access token to the JSON in responseContent and return both tokens, or it could decide per client whether to return accessToken or jwtAccessToken.
Additionally, the jti claim contained in a JWT-based access token matches the value of Authlete’s identifier access token.
A major advantage of JWT-based access tokens is that they do not require contacting the authorization server for revocation checking. However, in certain special scenarios, you may want to perform revocation and revocation checks even for JWT-based access tokens. For instance, you might prioritize performance by validating JWT-based tokens locally in general, but perform an additional revocation check with the authorization server for critical operations.
To implement revocation for JWT-based tokens issued by Authlete, it’s necessary to understand how Authlete handles them.
Authlete’s revocation endpoint (/auth/revocation) does not directly support JWT-type access tokens, so submitting a JWT token itself to the endpoint will not revoke it. If you want to revoke a JWT-based access token (i.e., mark it as revoked in Authlete’s internal database), you must send the identifier token contained in the JWT’s jti claim to the revocation endpoint.
### Cannot be revoked
POST https://example.authlete.com/api/auth/authorization/revocation
Authorization: {{API_Key/API_SECRET}}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"parameters": "eyJraWQiOiIxIiwiYWxnIjoiRVMyNTYifQ....&token_type_hint=access_token",
"clientId": "...",
"clientSecret": "..."
}
### Can be revoked
POST https://example.authlete.com/api/auth/authorization/revocation
Authorization: {{API_Key/API_SECRET}}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"parameters": "xx2rsI80DGVxlqKu1PWdxybR-7Ay6VjbMq01cwMbAFQ....&token_type_hint=access_token",
"clientId": "...",
"clientSecret": "..."
}
Regarding revocation checking, Authlete’s proprietary token introspection API (/auth/introspection) accepts JWT access tokens and verifies the database record based on the jti.
Therefore, if a JWT access token has been revoked using its jti claim, /auth/introspection will correctly reflect its revoked status.
On the other hand, /auth/introspection/standard only validates the JWT’s signature and expiration time and does not check the database record.
As a result, it does not perform revocation verification based on the jti claim.